Convexity Encephalocele
Convexity Encephalocele
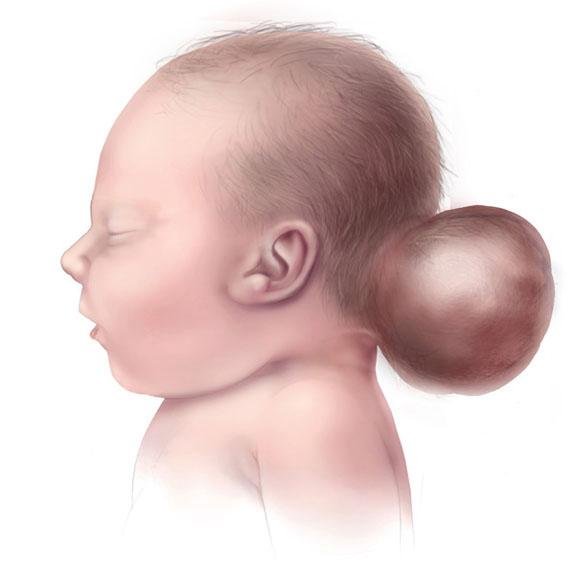
Convexity encephalocele is a rare type of neural tube defect (NTD) where part of the brain tissue, meninges (protective coverings of the brain), and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) herniate through a defect in the calvarial (skull) bone on the convex (outer) surface of the skull, often away from the midline. Unlike the more common occipital or frontoethmoidal encephaloceles, convexity encephaloceles may appear on the parietal, frontal, or temporal bones, making them less predictable and harder to detect prenatally. These anomalies are visible at birth as swelling or sac-like masses on the head and require early surgical intervention to prevent infection, protect brain tissue, and promote normal neurological development. 🌍 Convexity Encephalocele in the Bangladesh Context 🏥 Rare but reported among neonates, especially in rural districts with limited prenatal care 🤰 Often misdiagnosed as scalp cysts or tumors due to lack of fetal anomaly scans ⚠️ Risk of delayed referral, improper handling of the swelling, or infection 🧠 Parents may not realize the mass contains brain tissue 👨⚕️ Only a few pediatric neurosurgeons in Bangladesh have experience treating these cases At the National Institute of Neurosciences & Hospital (NINS) and Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre, Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman leads the management of complex congenital neurosurgical cases, including convexity encephaloceles, offering state-of-the-art care to patients from all over Bangladesh. ⚠️ Signs and Symptoms of Convexity Encephalocele 👶 Soft, compressible swelling on the scalp (usually present at birth) 🧠 May increase in size over time, especially with crying or straining 🩸 Thin, sometimes translucent skin over the mass 🧒 Neurological symptoms if functional brain tissue is involved 📉 Delayed milestones, seizures, or weakness in limbs (if left untreated) 💧 Risk of CSF leak or infection if the sac ruptures 🚨 Associated hydrocephalus in some cases 🧬 Causes and Risk Factors ❌ Incomplete closure of the neural tube during embryonic development 🥬 Maternal folic acid deficiency ☣️ Exposure to toxins, infections, or high fevers during pregnancy 🧬 Genetic mutations or syndromic cranial dysraphism 🏥 Lack of access to proper antenatal care and nutrition 🔍 Diagnostic Evaluation Accurate diagnosis is essential for successful surgical planning: 🧲 MRI Brain with spine screening – To assess contents of encephalocele and other brain/spinal anomalies 🦴 CT scan with 3D skull reconstruction – For bony defect localization 💉 Blood tests and neonatal metabolic screening (if required) 📈 Developmental and neurological assessment 🧬 Genetic counseling in cases with syndromic features “Convexity encephalocele may be rare, but with proper imaging, surgical planning, and skilled hands, it is a correctable condition that gives children the opportunity to live normally.” — Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman 🛠️ Surgical Management of Convexity Encephalocele Surgery is the definitive treatment and should ideally be done within the first few months of life, especially if the sac is large or prone to rupture. Surgical Objectives: ✅ Excise non-functional or necrotic brain tissue (if present) 🧠 Safely return viable brain tissue to the cranial cavity 🔒 Achieve watertight dural closure to prevent CSF leakage 🦴 Reconstruct skull defect to protect the brain 🛡️ Prevent infection and improve cosmetic outcome Surgical Steps: General anesthesia with neuro-monitoring Skin incision around the swelling Careful dissection and drainage of CSF Removal or repositioning of herniated content Dura mater repair Bone grafting or mesh cranioplasty as needed Cosmetic closure and layered wound repair ⏳ Surgery typically lasts 2–3 hours, depending on the size and complexity. 🏥 Postoperative Care and Follow-Up 🛌 NICU/Pediatric ICU monitoring for 1–2 days post-op 💉 Antibiotic prophylaxis and pain control 🧠 Regular neurological observation 🩺 Follow-up MRI/CT imaging at intervals 🧒 Developmental monitoring and early intervention programs 🔄 Prognosis and Long-Term Outlook Outcome depends on: 🧠 Whether functional brain tissue is involved ⏱️ Timing of surgery 🦴 Surgical precision and infection control 💡 Availability of follow-up care With early, skilled intervention, most children can achieve good functional and cosmetic outcomes. Neurodevelopmental support, physiotherapy, and parental education further improve long-term success. 👨⚕️ Why Choose Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman? 🧠 Expert in complex pediatric neural tube defect surgery 🏥 Operates at NINS – Bangladesh’s premier neurosurgery institute 🛠️ Advanced use of neuro-navigation, imaging, and sterile microsurgical technique 🤝 Offers holistic support through Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre ✅ Trusted by families from across Bangladesh for safe and compassionate care 📞 Get Expert Surgical Care for Convexity Encephalocele in Bangladesh Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman Assistant Professor, Pediatric Neurosurgery, NINS Chief Consultant, Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre 📱 For Serial/Appointments: 📞 01912988182 | 📞 01607033535 🌐 Visit: www.neurosurgeonnafaur.com
Encephalocele