Frontoethmoidal (sincipital)
Frontoethmoidal (sincipital)
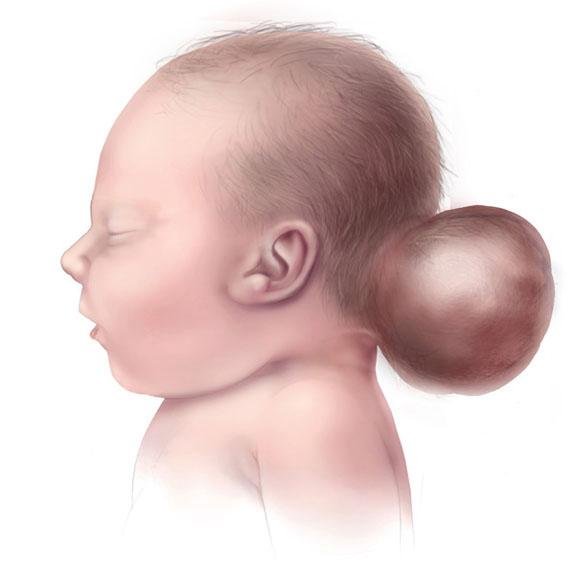
Frontoethmoidal encephalocele, also known as sincipital encephalocele, is a rare type of neural tube defect where a portion of the brain and its protective coverings (meninges) herniate through a bony defect at the junction of the frontal and ethmoid bones. This results in a visible swelling on the forehead, nasal bridge, or between the eyes—often present from birth. Unlike occipital encephaloceles that occur at the back of the head, frontoethmoidal encephaloceles affect the facial structure, potentially leading to disfigurement, eye misalignment, breathing difficulty, and neurological complications if left untreated. 🌍 Frontoethmoidal Encephalocele in the Context of Bangladesh In Bangladesh, this condition is more frequently seen due to: 🥬 Folic acid deficiency during early pregnancy 🤰 Limited or absent antenatal screening in rural and peri-urban areas 🏥 Delayed referral and misdiagnosis as a simple nasal mass or tumor 👨⚕️ Lack of access to specialized pediatric neurosurgical care Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman stands out as one of the few neurosurgeons in Bangladesh with substantial experience in managing this rare and complex congenital craniofacial anomaly. 🧠 Classification of Frontoethmoidal (Sincipital) Encephalocele There are three major types based on the location of the protrusion: Naso-frontal Encephalocele Mass appears at the root of the nose and forehead May distort the upper face Naso-ethmoidal Encephalocele Protrusion between the eyes; can widen the distance between them Naso-orbital Encephalocele Mass extends toward the eye socket; may displace the eyeball Each type affects facial symmetry, vision, and nasal passage function in varying degrees. ⚠️ Signs and Symptoms 🔵 Soft, compressible mass in the midline of forehead or nasal bridge 👁️ Hypertelorism (wide-set eyes) 💨 Nasal obstruction or breathing difficulty 🧠 Seizures or developmental delay (if brain tissue involved) 🦴 Skull bone defect confirmed on imaging 🧬 May be associated with other craniofacial or brain anomalies “A child’s face reflects their future. Treating frontoethmoidal encephalocele is not just surgery—it's a chance to restore normal growth and dignity.” — Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman 🔍 Diagnosis and Preoperative Assessment Timely and precise evaluation is key. Dr. Nafaur Rahman employs the following diagnostic tools: 🧲 MRI Brain & Skull – Determines the contents of the sac (CSF, meninges, brain tissue) 🦴 CT Scan with 3D Reconstruction – Defines skull base defect and plans bone reconstruction 📈 Neurological exam – Checks for vision, movement, reflexes, and development 🔬 Screening for associated anomalies or syndromes 🩺 Pediatric anesthetic and surgical risk evaluation before surgery 🛠️ Surgical Treatment Strategy Surgical correction is the only definitive treatment, aimed at both functional recovery and aesthetic restoration. Main Surgical Goals: 🧠 Excise nonfunctional neural tissue 🔧 Repair skull and dural defects to prevent CSF leakage 👃 Improve facial symmetry and nasal airflow ✅ Prevent future infection and neurological compromise Surgical Steps: Bicoronal scalp incision or midline approach Removal or repositioning of herniated brain/meningeal tissue Watertight dural closure to prevent CSF leak Skull base reconstruction using bone grafts or synthetic mesh Recontouring of forehead and nasal bridge if needed ⏱️ Surgery is ideally performed between 3–9 months of age, but can be done later in selected cases. 🏥 Postoperative Care and Recovery 🛌 Hospital stay: Usually 5–7 days 🧠 Close observation for CSF leak or infection 📈 Follow-up imaging to assess surgical outcome 👶 Pediatric rehabilitation for any developmental delays 👨⚕️ Long-term follow-up for growth, craniofacial symmetry, and neurological monitoring 🔄 Long-Term Outcomes Prognosis depends on: ✅ Size and content of the encephalocele 🔧 Precision of surgical repair 🧠 Presence or absence of functional brain in the sac 💡 Early diagnosis and management Most children go on to lead healthy, active lives when the surgery is performed correctly and timely by an experienced pediatric neurosurgeon. 👨⚕️ Why Choose Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman? 🧠 Specialist in rare congenital neurosurgical anomalies 🛠️ Proven experience in craniofacial neurosurgical reconstruction 🏥 Operates at National Institute of Neurosciences & Hospital (NINS) 🧒 Offers comprehensive, family-friendly care at Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre ✅ Works with plastic surgeons and ENT specialists for complete management 📞 Early Diagnosis = Better Outcome – Book a Consultation Now Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman Assistant Professor, Pediatric Neurosurgery, NINS Chief Consultant, Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre 📱 For Serial/Appointments: 📞 01912988182 | 📞 01607033535 🌐 Visit: www.neurosurgeonnafaur.com
Encephalocele