Occipital Encephalocele
Occipital Encephalocele
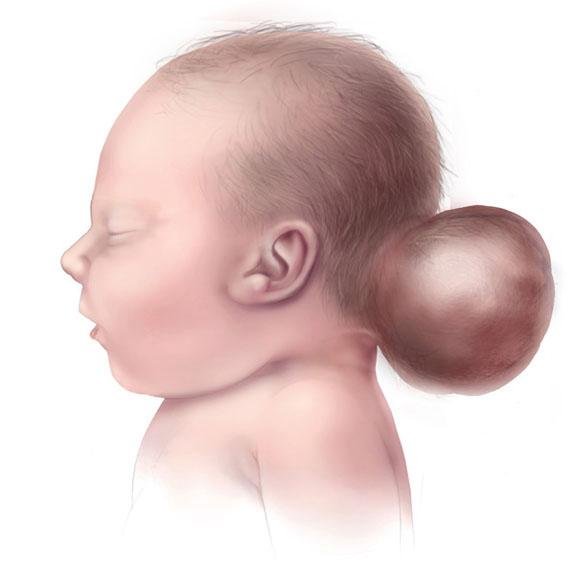
Occipital encephalocele is a rare neural tube defect in which part of the brain tissue and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) protrudes through a defect in the occipital bone (back of the skull). It results in a visible swelling or sac at the back of a newborn’s head, often present at birth. This congenital malformation is among the most common types of encephalocele and is a significant cause of neurological disability or death if left untreated. In Bangladesh, cases of occipital encephalocele are still reported frequently due to factors such as poor maternal nutrition, lack of folic acid supplementation, and limited access to prenatal screening. Early diagnosis and surgical intervention can drastically improve outcomes. 🌍 Occipital Encephalocele in the Bangladesh Context 🤰 High prevalence due to nutritional deficiencies during pregnancy 🧪 Limited fetal anomaly scans in rural and underserved areas 🏥 Lack of awareness and referral delay in managing visible congenital swellings 🧠 Shortage of pediatric neurosurgeons outside Dhaka or tertiary hospitals 🚸 Parents often confused between encephalocele and simple scalp swelling Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman, a renowned pediatric neurosurgeon in Bangladesh, has performed numerous successful surgeries on children with occipital encephaloceles—providing expert, child-friendly care with advanced neurosurgical techniques. ⚠️ Symptoms and Presentation Most cases are diagnosed at birth, but sometimes prenatal scans may reveal them. Key features include: 🎯 Visible swelling or sac at the back of the head 🌡️ Thin or translucent skin over the swelling 🧠 Protrusion may contain CSF, meninges, and sometimes brain tissue 🧒 Associated issues: hydrocephalus, microcephaly, motor delays 👁️ Eye movement problems, seizures, or vision impairment 🚼 Feeding difficulties, poor weight gain 🧬 May be linked to other syndromes or midline defects 🔍 Causes and Risk Factors ❌ Neural tube defect (NTD) due to incomplete skull bone closure during fetal development 🥬 Folic acid deficiency during early pregnancy 🧬 Genetic mutations or chromosomal anomalies ☣️ Maternal infections, diabetes, or environmental exposures 👩⚕️ Lack of antenatal care or delayed diagnosis 🧪 Diagnostic Workup Pre-surgical imaging and evaluation are critical to determine the extent of brain involvement: 🧲 MRI Brain – To assess herniated brain structures and associated abnormalities 🧠 CT scan (3D) – For bone defect localization 🧬 Genetic evaluation – If syndromic features are suspected 🍼 Neonatal assessment – For hydrocephalus, breathing, feeding, and reflexes 📈 Neurological examination and head circumference measurement 🛠️ Surgical Treatment for Occipital Encephalocele Surgery is the only definitive treatment, and timing is essential: Goals of Surgery: 🔧 Remove nonfunctional brain tissue (if present) 🔒 Repair skull and dura defect 🛡️ Protect brain from infection and trauma ✅ Restore CSF dynamics and prevent hydrocephalus Surgical Technique: Under general anesthesia Incision made over the sac Herniated sac is dissected and excised Dura (membrane around brain) is repaired watertight Skull defect may be reconstructed (cranioplasty) CSF diversion via VP Shunt may be done if hydrocephalus is present ⏱️ Ideal age for surgery: As early as medically safe, typically within the first few months of life 🔄 Postoperative Care and Follow-Up 🛌 Hospital stay: 5–7 days 💉 Antibiotics and fluid management 🧠 Monitor for seizures or neurological signs 📈 Follow-up imaging to check CSF flow 🧒 Developmental assessments, physiotherapy, and pediatric neurology support 💡 Long-Term Outcomes Prognosis depends on: 📊 Size and contents of encephalocele 🧠 Presence of functional brain tissue in sac ⚖️ Associated anomalies or syndromes ⏳ Timing and completeness of surgical repair With expert surgery and multidisciplinary support, many children can survive and thrive, especially those with small, non-brain-containing sacs. “Every encephalocele we repair is a life given hope and dignity. Early surgery, expert hands, and family trust make all the difference.” — Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman 👨⚕️ Why Choose Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman? 🧠 Experienced in complex congenital neurosurgical repairs 🏥 Works at Bangladesh’s largest neurosurgical center – NINS 🔬 Uses advanced microsurgical and neuro-monitoring tools 🧒 Provides compassionate, family-centered care through Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre ✅ High success rate in neonatal and infant encephalocele surgeries 📞 Book Expert Consultation Today Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman Assistant Professor, Pediatric Neurosurgery, NINS Chief Consultant, Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre 📱 For Serial/Appointments: 📞 01912988182 | 📞 01607033535 🌐 Visit: www.neurosurgeonnafaur.com