Cerebral TB
Cerebral TB
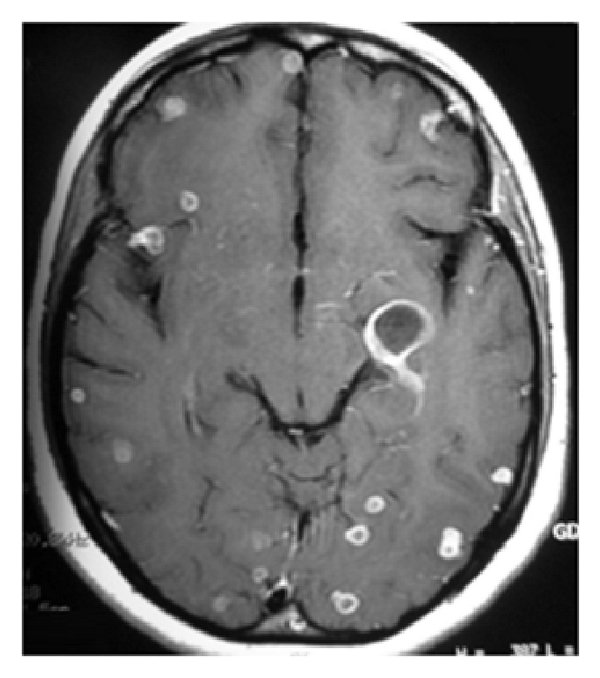
Tuberculosis (TB) is one of the most prevalent infectious diseases worldwide and accounts for significant morbidity and mortality. The three major stages of tuberculosis are exposure, infection, and disease. For children, the most likely exposure is from someone with infectious tuberculosis in the household, but exposure may occur in the school or daycare setting as well. CNS TB develops when M. tuberculosis spreads hematogenously to the brain, meninges, and spinal cord, resulting primarily in tuberculous meningitis, tuberculoma, tuberculous abscess, and tuberculosis of the spine. Tuberculous meningitis is a life-threatening condition. It rarely occurs in infants under 4 months of age and is most common in children under the age of 6 years. TB meningitis usually presents within 2 to 6 months after the initial infection.
Presentations
- Fever
- Meningismus
- Seizures
- Vomiting
- Hemiparesis
- Altered level of consciousness
- Bulging fontanelle in infants